Insights - How to Create your Strategyzer Business Model Canvas.
How to Create your Strategyzer Business Model Canvas.
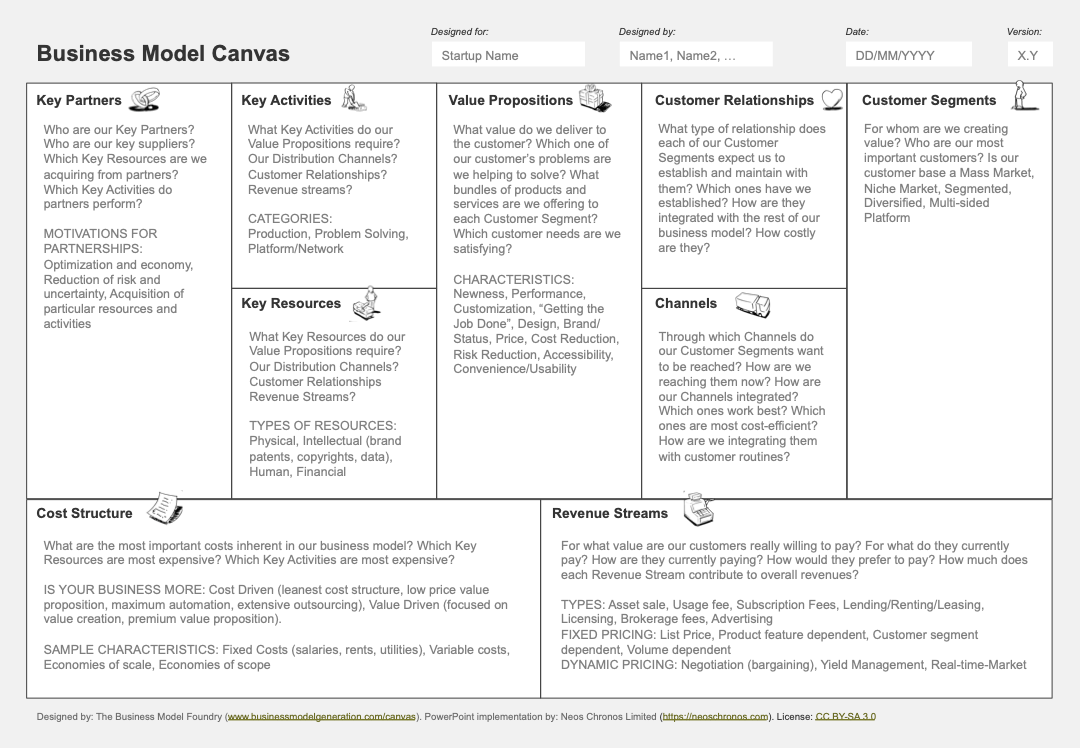
A business model describes how a company creates, delivers, captures, and defends value. While this definition may sound complicated, defining, and developing a business model does not have to be a daunting task. In this step-by-step guide, we will share with you a proven process to follow, as well as questions and checklists to help you avoid common pitfalls. We will be using the Business Model Canvas from Strategyzer as our tool, which you can download from our Template Library. Let's get started!
![]()
CHOOSE AN IDEA
Everything starts with your business idea. Your idea may be around a problem that people encounter in daily life and you believe you can solve it. Sometimes, your idea will be about a solution to a problem that is obvious to you, but everyone seems to miss it. In rare cases, your idea will be so unique that it may disrupt an industry. There is no need to write it down separately, it will be depicted on the Business Model Canvas (BMC). It is helpful to give your business a provisory name and fill this in the appropriate fields at the top of the Business Model Canvas.
![]()
DEFINE CUSTOMERS AND USERS
As a next step, you should define who are the people that will pay to benefit from your idea, and who are the people that will use products and services related to your idea. These are referred to as Customer Segments. Sometimes customers and users are the same people, e.g. the buyer of a loaf of bread in a bakery. Sometimes customers and users differ. On social media networks, for example, the users are the members, however, the customers are the advertisers that want to reach those members. Write down a short description of customers and users. Think about where they live, how much money they earn, how their daily life looks like, and their dreams and aspirations. Start with a short description, and extend every time you learn something more about them. You can use a Customer Personas Canvas for this purpose.
![]()
ARTICULATE YOUR VALUE PROPOSITIONS
A value proposition (VP) is a statement that says to a customer and user why you are different and worth paying attention to. The key here is to focus on the benefits you deliver to customers and users first. It is a good practice to create a list of value propositions and then keep working on refining them for the target segment. To get started you may want to use the following template.
At company name we enable customer segments to achieve list of benefits by offering a solution that solves their list of problems in a differentiated way compared to existing alternatives.
When talking to customers, you may want to stop at benefits. When talking to investors, you may have to use the full version.
If you want to go deeper in defining a value proposition, you can use the Value Proposition Canvas by Peter J. Thomson to help you structure your thinking. This canvas is optimised to capture the needs, wants, and fears of a segment, and enable you to determine how your features, benefits, and experience address those.
![]()
DESCRIBE POTENTIAL REVENUE STREAMS
Customer willingness to pay is the ultimate validation of a value proposition's strength i.e. whether it is a must-have (very valuable) or nice-to-have (less valuable). It is a well-known fact that the existence of competition is often validation that a market and revenue potential exists. So do research existing alternatives to get a reference view on potential revenue streams. Talk to potential customers and gauge their willingness to pay. If customers perceive the value proposition you offer as a must-have, it is not uncommon that they will be willing to preorder from you. Capture how much, how often, and in which ways customers would be willing to pay and note it down in this block of the canvas. Ensure you have sufficient indications from your research that customers regard your value propositions as must-haves before moving further.
![]()
CHOOSE YOUR CHANNELS TO MARKET
Equipped with the knowledge that customers are willing to pay for your value proposition, it is now time to decide your initial channel approach i.e. how you are going to reach these segments. You should already have ideas from your knowledge of how existing alternatives are reaching the market. Or you may want to completely rethink the channels to the market. Whichever holds true for you, rest assured that you are going to be optimising your choice over time. Typically, you want to capture in this block the channel type and all resources, activities, and partners you will need to be present at each online and offline place the customer comes in contact with your product or service. You can use a Channel Implementation Canvas for this purpose.
![]()
DEFINE CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIPS
Depending on the experience you want to offer to your customer segments, in this step you need to define what type of relationships you want to build. Are you going to build a direct B2B or B2C relationship or an indirect one through resellers? Will your interaction with customers and users be human-centric, automated, or both? Note down the associated keywords to define the type of relationship for each customer segment, and if you used a Channel Implementation Canvas update it with the additional information.
![]()
LIST KEY ACTIVITIES
With your defined set of value propositions, chosen channels, and customer relationships, you can now list the key activities that you are going to execute. The qualification "key" denotes those activities that are crucial to the creation of the value proposition, the smooth delivery of the product or service to market through the chosen channel, and the establishment of a strong customer relationship. By inference, key activities, when performed well, should result in a significant advantage or differentiation for your value proposition and business model. Decide which of those activities should be performed and managed by your staff and which could be outsourced.
![]()
IDENTIFY KEY RESOURCES
Having identified the key activities, the next step is to identify the resources you will need to perform these activities. Such resources could be people, processes, tools, intellectual property rights, money, ... etc. Similar to key activities, decide which key resources should be owned and managed directly by your company and which could be supplied by 3rd parties.
![]()
CONSIDER KEY PARTNERS
Key partners strengthen the ability of a company to create and deliver a value proposition and capture the associated revenue. Typical examples include hardware companies using key manufacturing partners to optimise production cost, national companies using international representatives to accelerate channel expansion, ... etc. Note down the partners you are going to use who can perform the key activities, and can provide the key resources your business model needs better than you can.
![]()
UNDERSTAND THE COST STRUCTURE
The cost structure primarily reflects fixed and variable costs for running the company (General & Administration), creating the value proposition (Research & Development), and operating the channels to market (Sales & Marketing). It is good practice to create a financial plan to determine the amount of money required monthly to perform all these tasks (Burn Rate). Knowing your Burn Rate is mandatory in case you would like to ask for investment to be able to operate for a defined period without depending on revenue (Runway). It is even better to determine the unit economics of your value proposition. That is understanding the revenue as well as the cost associated with the most basic sales object e.g. one item of a physical product, a monthly subscription fee, ..., etc. With these you can easily determine: profit per unit, the number of units to be sold to reach positive cash flow (the state where you do not eat up your company's cash reserves), the number of units to reach break-even, etc. Give yourself some time to do this, and capture your unit economics in this block as well as the block for Revenue Streams.
IN SUMMARY
In this step-by-step guide, we shared with you a proven process to follow to create your business model with the Business Model Canvas. Adopting our recommendations will help you avoid common pitfalls and progress faster on your entrepreneurial journey.
Good luck!
CREDITS & REFERENCES
For the avoidance of doubt, Neos Chronos is not affiliated with and has no financial interest in any of the companies mentioned in this article. All names and trademarks mentioned herein are the property of their respective owners. Please observe the Neos Chronos Terms of Use.
- Neos Chronos Business Model Canvas Workshop
- Neos Chronos Lean Canvas Workshop
- Neos Chronos Template Library
INTRIGUED?
For more information on how our advisory services can help you accelerate your entrepreneurial journey, please contact us to arrange an introductory meeting or
Book a Discovery Session now!
Get to know us. Put us to the test.